This post may contain paid links to my personal recommendations that help to support the site!
You’re here because of all the confusion between a business analyst and a business intelligence (BI) analyst. The same question still remains: what is the difference between a business analyst and a BI analyst?
I’ve done some research here’s the short answer:
A business analyst improves processes and functions of businesses using data analysis but a business intelligence (BI) analyst drives business decisions through data warehousing. Both the business analyst and the BI analyst roles are also different in their work processes, type of data, type of analysis, and tools used.
Now that you’re clearer on the main differences, you might be curious to know exactly how they differ in more detail.
I’ve compiled the comparison in the table below:
| Factor | Business Analyst | Business Intelligence Analyst | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Definition | Improves business processes, procedures, and products through data analysis. | Discovers business-focused insights that lead business decisions using data warehousing and BI tools. |
| 2 | Process | Defining scopes of business objectives, planning business requirements, implementing a solution, and evaluating the solution. | Understanding the needs of the business end-user, querying from the respective databases, and joining them to derive insight. |
| 3 | Type of Data | Unstructured and structured data | Structured data |
| 4 | Type of Analysis | Investigational, specific, and ad-hoc analysis | Structured and periodical analysis |
| 5 | Skills and Tools Required | Drawing tools Business analysis Excel SQL | SQL Excel Tableau/Power BI ETL tools |
| 6 | Education Level | Bachelor’s Degree | Bachelor’s Degree |
| 7 | Salary | USD $70,644 (US) | USD $71,050 (US) |
Now that you’re clearer on the main differences, let’s have a deeper look into why these 2 jobs are actually quite different!
1. Definition
Firstly, the 2 roles are quite different in definition:
| 1 | Business Analyst | Business Intelligence Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Improves business processes, procedures, and products through data analysis. | Discovers business-focused insights that lead business decisions using data warehousing and BI tools. |
If you look at each role closely, there’s actually much to compare in their definition!
Here’s why:
A business analyst focuses on processes more than a BI analyst would. They typically take a single problem in a business process and try to refine that!
a) Business Analyst
Here’s a video I found from BA Tutor that best explains a typical business analyst:
To summarize the video, business analysts zoom in on a business process and become the middleman between the IT/engineering department and the business department.
They communicate between the two to sharpen business processes.
I’d highly recommend checking out his channel for more useful information on business analysts!
He’s one of my favorites on my full list of business analyst YouTube channels.
Now let’s contrast it with a BI analyst!
b) Business Intelligence Analyst
Although you’d think that a role with such a similar name would be close to what a business analyst does, BI analysts are actually more similar to data analysts than business analysts.
Here’s why:
BI analysts work with all aspects of data within a business to create and maintain data warehouses. These data warehouses create a central location for querying data and creating BI dashboards for business-focused insight.
This means that BI analysts are more general analysts that orchestrate data within a business with the aim of providing business insight.
By this definition, that makes BI analysts more similar to data analysts than business analysts!
For more on that comparison of BI analysts and data analysts, you can read this article I wrote.
2. Process
Both roles have very similar processes, with some minor differences.
| 2 | Business Analyst | Business Intelligence Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Defining scopes of business objectives, planning business requirements, implementing a solution, and evaluating the solution. | Understanding the needs of the business end-user, querying from the respective databases, and joining them to derive insight. |
Let’s have a look at each role in greater detail.
a) Business Analyst
Business analysts focus more on the practical applications and the outcomes of the business problem, instead of the technical data side.
Here’s how a more detailed business analyst process usually goes:
- Defining the scope of business objective
- Planning business requirements
- Communicating solutions to IT departments
- Implementing solution
- Evaluating solution
- Maintaining solution
However, this might vary among business analysts in different companies and industries.
For example, in a tech company, a business analyst may follow very closely to the Systems Development Lifecycle.
This video below covers that process quite well:
In this process, a business analyst may contribute to a business in these ways:
- Forming a detailed business analysis
- Forecasting and data modeling
- Identifying opportunities for a business
- Monitoring pricing
This is pretty similar to how a BI analyst works. Let’s explore their processes below.
b) Business Intelligence Analyst
BI analysts handle more of the data side of things than business analysts do.
Here’s the typical process of a BI analyst:
- Understanding the needs of end-users
- Defining the main business problem
- Gathering, querying, and joining relevant data sources
- Transforming and cleaning data
- Visualizing data on dashboards
- Delivering business insight feedback to end-users
As you can see, many of the steps involve handling data. This is what makes a BI analyst a more technical role than a business analyst!
If you’d like to learn more about BI analysts, you might want to check out my list of the best business intelligence YouTube channels!
3. Type of Data
| 3 | Business Analyst | Business Intelligence Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Type of Data | Unstructured and structured data | Structured data |
Data matters a lot to both analysts but they tend to deal with data that comes from different sources, leading to the difference in the type of data.
Let me explain each role in detail:
a) Business Analyst
A business analyst deals with both unstructured and structured data. This is highly dependent on the business objectives and the project they’re working on.
Why’s that?
Well, business analysts tend to work on processes that aren’t that ironed out and need improvement – that’s what they’re there for!
This means that bad quality data is involved. When a process is undefined, data tends to be collected and stored in an uncontrolled manner.
Some data can be stored in silos within separate Excel sheets.
Others may be photos or images that aren’t stored in a central location. In this case, the analysis is more qualitative than quantitative.
b) Business Intelligence Analyst
BI analysts are mostly quantitative that deal with structured data.
Some common data sources for BI analysts include:
- Data warehouses
- Structured relational databases
- Organized flat files (Excel, CSV files)
The type of data used by BI analysts from these sources is very much different from those used by business analysts.
That’s because the type of analysis that’s done for each role is different too!
Let’s look at that for our next point below.
4. Type of Analysis
| 4 | Business Analyst | Business Intelligence Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Type of Analysis | Investigational, project-based, and ad-hoc analysis | Structured and periodical analysis |
a) Business Analyst
The type of analysis done by a business analysis is investigational in nature.
Because of their focus on specific projects or processes, any data analysis done by business analysts is likely to be ad-hoc and quicker.
Also, some business analysts may not even do any heavy data analysis work altogether!
Instead, they focus on defining business problems by creating business analysis charts.
These charts may include:
- Process mapping
- Process flows
- Waterfall charts
And here’s a good video introduction to process mapping commonly used by business analysts:
b) Business Intelligence Analyst
On the other hand, BI analysts have more structured and thought-out analyses.
You’ll most often hear of BI analysts getting business requests to carry out regular periodical reporting and providing continual visibility on KPIs on dashboards.
Due to the need for accuracy of these data, these requests tend to be more long and drawn out.
Although BI analysts do have ad-hoc analysis tasks, they do more work that requires handling structured data because of their skill in business intelligence tools like SQL and Tableau.
5. Skills and Tools Required
| 5 | Business Analyst | Business Intelligence Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Skills and Tools Required | Drawing tools Business Analysis Excel SQL | SQL Excel Tableau/Power BI ETL tools |
a) Business Analyst
Business analysts have a much more balanced skillset than BI analysts.
Here’s why:
Business analysts need to be proficient in both soft and hard skills. They are required to deliver business requirements and technical requirements between teams, which requires a strong understanding of both sides of the business.
Other than the skills shown in the table above, you might also encounter some business analysts with SQL knowledge.
However, according to my analysis of the Stack Overflow Survey, only 27% of business analysts know SQL.
Curious to know more about whether SQL is required for business analysts?
You can read more in this article here.
b) Business Intelligence Analyst
BI analysts also require some level of people skills but they are better known for being more technical.
Therefore, a more detailed list of skills of a BI analyst will look something like this:
- SQL
- Excel
- Google Sheets
- Tableau
- Power BI
- Amazon S3 Data Warehouse
- Google Cloud
- ETL tools
Therefore, you can say that BI analysts possess more technical skills than business analysts!
Here’s a great video covering the essential skills used in BI:
6. Education Level
| 6 | Business Analyst | Business Intelligence Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Education Level | Bachelor’s Degree | Bachelor’s Degree |
Education levels are actually surprisingly similar for both business analysts and BI analysts!
Currently, both business analysts and BI analysts require Bachelor’s degrees to get an entry-level job.
However, this might be changing soon!
More employers are now seeking skills instead of degrees and this requirement for a Bachelor’s degree may become irrelevant in the near future!
With the introduction of professional certificates like the Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate and the IBM Data Analyst Professional Certificate, more learners like you can also break into the field without Bachelor’s degrees!
However, this may vary among jobs!
Here’s why:
Due of the highly technical nature of the BI analyst, some companies may request for a relevant Masters’ degree in a technical domain.
7. Salary
With both roles being in the tech domain, both business analysts and BI analysts enjoy a pretty high average starting salary!
| 7 | Business Analyst | Business Intelligence Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Salary | USD $70,644 (US) | USD $71,050 (US) |
However, these figures shown above may vary depending on your location and state, if you’re based in the US.
a) Business Analyst
Let’s have a look at what Payscale says about the business analyst salary!
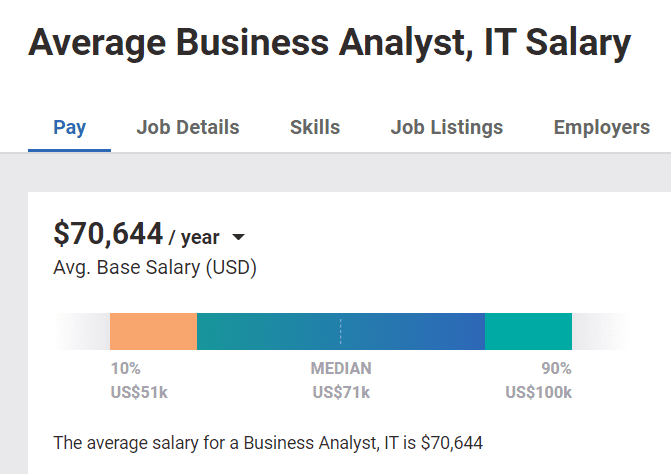
According to Payscale, a business analyst in the US earns an average of USD $70,644 per year.
However, I believe that this salary is high because smaller companies with less capital to hire business analysts tend to hire less.
Therefore, this salary might be skewed towards large organizations, which may inflate the salary average.
b) Business Intelligence Analyst
BI analyst salaries are pretty similar to business analyst salaries.
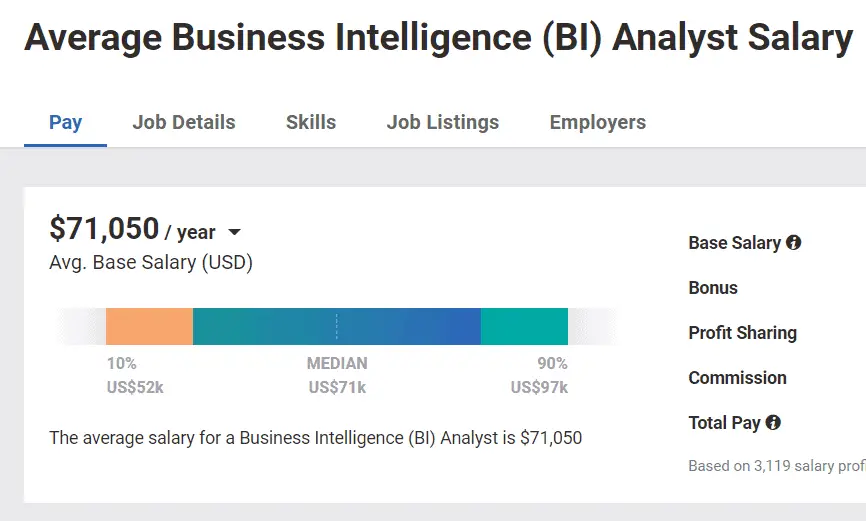
According to Payscale, a BI analyst in the US earns an average of USD $71,050 per year.
This is coming in at a slightly higher salary than the business analyst!
Here’s why I believe BI analysts might be paid higher:
BI analysts require more technical training and would naturally hire individuals with more years of experience than business analysts.
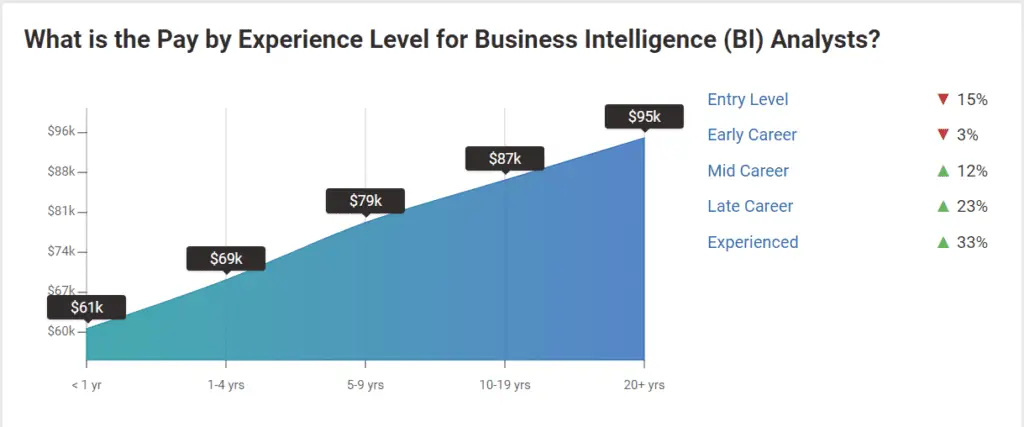
Based on this infographic above by Payscale, you can see that there are more BI analysts in the late-career to experienced levels than entry-level.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is a Business Analyst the Same as a Business Intelligence Analyst?
A business analyst is not the same as a business intelligence analyst. A business analyst improves business processes using data analysis but a business intelligence (BI) analyst drives business decisions through data warehousing. They differ in their work processes, type of data, type of analysis, and tools used.
Who Earns More: Business Analysts or Business Intelligence Analysts?
Business intelligence analysts earn more than business analysts. According to Payscale, BI analysts earn USD $71,050/year but business analysts earn $70,644/year. However, BI analysts do not earn much more than business analysts, and BI analysts require technical experience and are skewed toward late-career individuals.
Which is Better: A Business Analyst or Business Intelligence Analyst?
A business intelligence analyst is better than a business analyst. BI analysts have a better career progression in the data field and have better future prospects. However, BI analysts require more technical work experience. Moreover, business analysts are also irreplaceable for their excellent people skills.
What Is The Difference Between Business Analysis and Business Intelligence?
Business analysis involves analyzing and improving business processes using data analysis but business intelligence involves driving business decisions using data gathered and analyzed from across the business. However, both of them are similar in their purpose – to improve businesses.
What Is The Difference Between a Data Analyst and a Business Intelligence Analyst?
A data analyst solves problems only through analytics but a business intelligence analyst discovers business-focused insights through data. Both roles are relatively similar in definition, process, type of data, and type of analysis, except for the type of tools used, which may vary slightly.
Read the full comparison of the two roles over here.
Final Thoughts
That’s about all the differences and questions regarding business analysts vs BI analysts! I hope this comparison has helped clear the air on all your confusion between the two roles!
Thanks for reading!
My Favorite Learning Resources:
My Recommended Learning Platforms!
| Learning Platform | What’s Good About the Platform? | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Coursera | Certificates are offered by popular learning institutes and companies like Google & IBM |
| 2 | DataCamp | Comes with an integrated coding platform, great for beginners! |
| 3 | Pluralsight | Strong focus on data skills, taught by industry experts |
| 4 | Stratascratch | Learn faster by doing real interview coding practices for data science |
| 5 | Udacity | High-quality, comprehensive courses |
My Recommended Online Courses + Books!
| Topic | Online Courses | Books | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Data Analytics | Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate | – |
| 2 | Data Science | IBM Data Science Professional Certificate | – |
| 3 | Excel | Excel Skills for Business Specialization | – |
| 4 | Python | Python for Everybody Specialization | Python for Data Analysis |
| 5 | SQL | Introduction to SQL | SQL: The Ultimate Beginners Guide: Learn SQL Today |
| 6 | Tableau | Data Visualization with Tableau | Practical Tableau |
| 7 | Power BI | Getting Started with Power BI Desktop | Beginning Microsoft Power BI |
| 8 | R Programming | Data Science: Foundations using R Specialization | Learning R |
| 9 | Data Visualization | – | Big Book of Dashboards |

